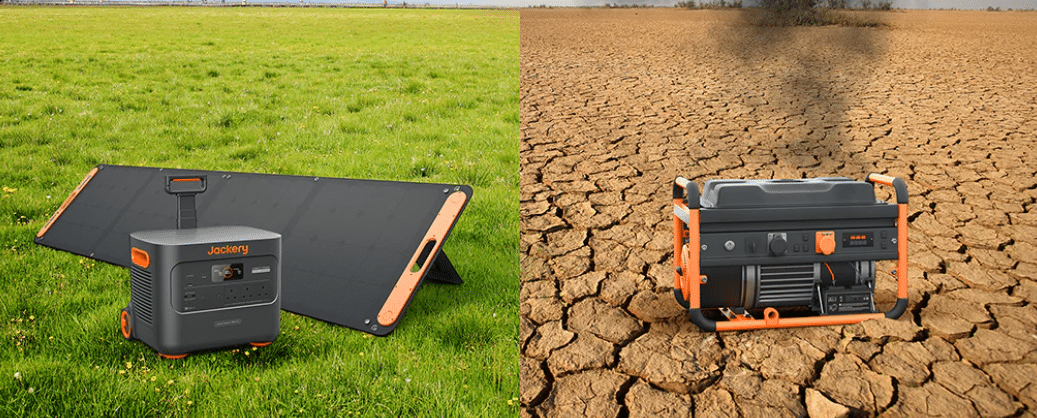
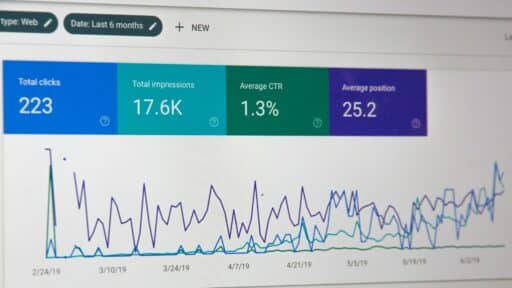
Introduction: What is a Home Generator?
In simple terms, a household generator is a device that provides backup or supplementary power for homes. When the power grid fails or power is insufficient, the generator can quickly step in to ensure household lighting, appliance operation, and basic living needs.Currently in the UK, common household generators can be roughly divided into two categories.
The first is the traditional fuel generator, which typically uses gasoline, diesel, or natural gas as fuel. These devices have high power and can provide long-term power support, and are commonly used in scenarios where the entire house needs power or a long-term backup power source.
The second is the portable energy storage power supply that has developed rapidly in recent years. It uses clean energy technologies such as lithium batteries and is charged through mains electricity or solar energy. When needed, it outputs power through AC sockets or USB interfaces. Energy storage power supplies are noiseless and have no exhaust emissions during use, making them more environmentally friendly and more suitable for modern households and urban environments.
It can be said that the concept of household generators is no longer limited to traditional “oil generators” but is gradually evolving towards clean, intelligent, and multi-scenario applications.
Global and UK Market Overview
Globally, the home generator market is significant and growing. Europe, including the UK, represents the world’s second-largest generator market. In 2024, the revenue of the European home generator market reached approximately USD 1.8 billion. The UK’s market alone was valued at USD 1.59 billion in 2025, with forecasts predicting growth to USD 2.5 billion by 2030, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 9.5%.
Meanwhile, consumer demand is shifting. Traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) generators are experiencing decline: in 2024, consumption fell to 3.3 million units (–4.5% year-on-year), with market value dropping 7.6% to USD 221 million. Conversely, portable generators—especially lithium-battery storage solutions—are on the rise, with market value at USD 3.8 billion in 2024 and expected to reach USD 6.2 billion by 2030 (CAGR 8.1%). This reflects a broader transition toward eco-friendly, flexible, and portable power solutions.
| Metric | Data / Trend |
|---|---|
| Europe Home Generator Revenue (2024) | USD 1.8 billion (2nd largest after North America) |
| UK Generator Market Value (2025) | USD 1.59 billion; projected to grow to USD 2.50 billion by 2030 (CAGR ~9.5%) |
| Internal Combustion Generator Usage | Declining—3.3 M units (-4.5%), USD 221 M (-7.6%) in 2024 |
| Portable Generator Market (UK) | Valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2024; expected to reach USD 6.2 billion by 2030 (CAGR 8.1%) |
| Growth Drivers | Electricity disruptions, residential/construction sector demand |
Why Do We Need Home Generators?
There are several compelling reasons why UK households increasingly view home generators as essential:
- Unreliable Power Supply and Outages: Although the UK’s grid is relatively stable, severe weather events—such as storms, floods, and heatwaves—are increasing. These events often lead to regional blackouts. Having a home generator ensures continuity for heating, refrigeration, lighting, and digital connectivity.
- Energy Security Concerns: The geopolitical landscape, especially the Russia-Ukraine war, has raised worries about Europe’s energy reliability. Dependence on imported gas and rising energy costs make self-sufficiency an attractive option.
- Environmental Transition: The UK government is strongly pushing for carbon neutrality and renewable adoption. This transition, while necessary, sometimes creates transitional instability. Consumers are seeking greener backup solutions to complement the national energy shift.
- Lifestyle Evolution: Modern households depend heavily on electricity—not just for essentials, but for lifestyle devices. Remote work, smart home systems, and entertainment setups mean that losing power can disrupt both productivity and comfort.
How to Choose a Home Generator
Selecting the right generator depends on household size, lifestyle, and specific needs. Key considerations include:
- Capacity: Small households may only need backup battery for lighting, internet routers, and basic appliances, while larger families may want whole-house support.
- Portability: Some families prefer stationary home units, but many now opt for portable solutions they can use at home, on trips, or during camping.
- Power Source: Traditional fuel generators are strong in raw output, but battery-based models are quieter, cleaner, and easier to maintain.
- Smart Features: Many modern generators integrate with mobile apps, enabling remote monitoring and control.
- Safety and Sustainability: Eco-friendly, low-noise, and emissions-free generators are increasingly prioritized by UK consumers.
Jackery Generators: Practical Solutions for UK Homes
Jackery, a global leader in portable power, offers solar generators designed for modern needs. Their products combine clean lithium-battery technology, solar charging, and portability. Here are three key models ideal for UK households:
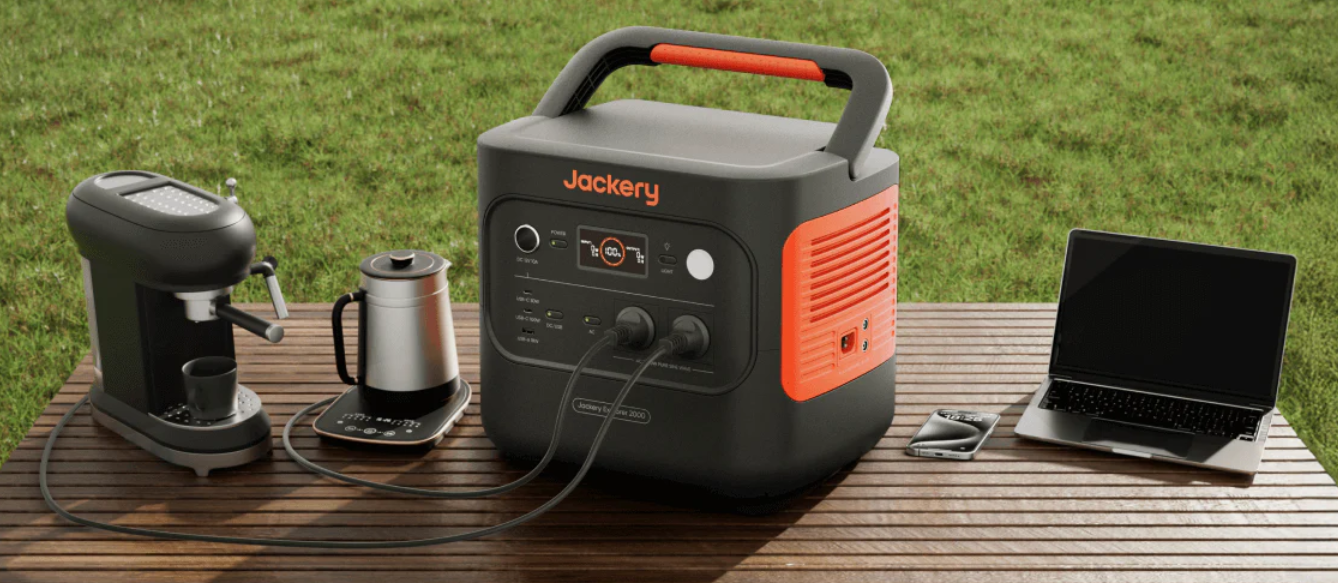

1. Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus is a flagship model ideal for families seeking reliable whole-home backup. It delivers up to 2042Wh capacity with expandable options reaching over 12kWh when paired with battery packs. This means it can support essentials like refrigerators, washing machines, and multiple devices simultaneously.
With high solar input (up to 3000W), households can quickly recharge during the day, making it a sustainable and cost-effective solution. Its smart app integration allows users to monitor and control charging status in real time.
2. Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Pro
For mid-sized households or those who want a balance between capacity and portability, the Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Pro is an excellent option.
It provides 1002Wh of power and supports a wide range of outputs, including USB-A, USB-C, and AC ports. It’s particularly suited for emergency use during power outage or for powering essential appliances like laptops, lights, routers, and small kitchen devices. The unit recharges fully in just 1.8 hours via AC, ensuring quick turnaround for repeated use.

3. Jackery Solar Generator 500
For smaller households, students, or couples, the Jackery Solar Generator 500 offers a more compact solution. With 518Wh capacity, it’s perfect for running small electronics, communication devices, and essential lighting.
Its lightweight design makes it not only useful during outages but also ideal for camping and outdoor activities. Despite its compact size, it still features multiple output ports and solar compatibility, ensuring flexibility for various scenarios.

Practical Planning for Households
When considering a home generator, households should start by identifying their core needs:
- Essentials Only: Focus on a generator in the 500–1000Wh range to support routers, lighting, and small appliances.
- Family Comfort: Opt for models like the 1000 Pro that balance portability with higher capacity, ensuring refrigerators and multiple devices stay powered.
- Whole-House Backup: Larger families or those in rural areas may need high-capacity solutions like the 2000 Plus, potentially with expansion packs for long-term outages.
Beyond these broad categories, a more detailed planning framework helps you choose with confidence:
1) Define outage scenarios and runtime targets.
List the most likely events you face (winter storms, flooding, planned maintenance). For each, estimate a realistic maximum duration (e.g., 4–6 hours, 12–24 hours, multi-day). A simple rule of thumb is to size for 1.2–1.5× your expected daily consumption during an outage to account for inverter losses, cold weather efficiency drops, and unplanned loads.
2) Build a priority load budget.
Identify the devices you cannot lose: broadband router (10–30W), phones/laptops (20–150W while charging), LED lighting (5–10W per bulb), fridge/freezer (60–120W running, higher at start-up), medical devices (follow manufacturer specs), and one or two comfort loads (e.g., kettle/microwave/induction hob used intermittently).
Add their simultaneous wattage to determine inverter needs, and their daily watt-hours to size capacity. If you want hot drinks or basic cooking during an outage, plan to use these appliances in short sessions to keep total energy demand reasonable.
3) Match capacity and expandability to your lifestyle.
- Flat-dwellers & couples: A 500–1000Wh unit keeps communications, lighting, and a compact fridge going through short outages. Portability is key when storage space is limited.
- Families with children: Step up to 1–2kWh so you can run a full-size fridge/freezer, charge multiple devices, and maintain lights/Wi‑Fi without strict rationing.
- Households with critical medical equipment: Prioritize redundancy and monitoring. Consider the 2kWh class with expansion packs, plus clear operating procedures and periodic testing.
- Rural homes / frequent outages: Look for 2–3kWh base capacity with solar input and optional expansion (≥6–12kWh) to ride out multi‑day disruptions.
- Renters & students: Choose lightweight, quiet, and UKCA‑marked units; avoid any installation that would require landlord approval.
4) Plan charging pathways.
Diversify between mains (AC) charging, vehicle charging, and solar input. In the UK’s climate, south-facing panels with a 20–40° tilt perform well year-round; avoid shading from chimneys or trees. Consider portable, folding panels if roof installation is not an option. For balcony setups, check IP ratings, wind resistance, and cable routing safety.
5) Evaluate total cost of ownership (TCO).
Beyond the purchase price, factor in maintenance (filters, oil for ICE units; firmware and occasional battery health checks for lithium systems), projected battery cycle life, potential savings from solar charging, and warranty support. Well‑sized battery generators often deliver superior lifetime value due to near‑zero fuel cost and minimal servicing.
6) Sustainability and end‑of‑life.
Prefer LiFePO₄ chemistry where available for longevity and stability, pair with solar wherever practical, and plan responsible battery recycling. Right‑sizing your system (not over‑specifying) is both economical and environmentally prudent.
Illustrative picks using the Jackery range:
- Essentials‑only starter → Jackery Solar Generator 500: multi‑port, ideal for comms and lights.
- Balanced family setup → Jackery Solar Generator 1000 v2: handles a fridge plus devices with fast AC recharge.
- Scalable resilience → Jackery Solar Generator 2000 v2-ready for long outages; strong solar input and smart monitoring.
Conclusion
The UK home generator landscape is changing fast. Market growth is robust, but the composition of that growth is even more telling: internal combustion units are steadily giving way to quiet, solar‑ready, battery‑based systems that better align with urban living, noise limits, and decarbonisation goals. This shift is not just technological—it reflects how households think about resilience, comfort, and environmental responsibility.
From a practical standpoint, selecting the right system starts with understanding your outage profile and priority loads. Size for your real needs, choose proven safety features and certifications (e.g., UKCA), and design multiple charging pathways so your backup is ready when you need it most. Integration can be as simple as extension leads to critical devices, or as refined as a transfer‑switch‑based sub‑panel installed by a qualified electrician. For many families, pairing storage with solar is the most future‑proof path: it offers clean energy year‑round, trims electricity bills, and delivers dependable autonomy during blackouts.
In that context, modern solar generators exemplify the new standard. A compact unit like the Jackery Solar Generator 500 keeps communications and lighting stable; the Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Pro balances portability with the ability to run a refrigerator and multiple devices; and the Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus brings genuine resilience with expandable capacity and strong solar intake for multi‑day events. Together, they demonstrate how modular design lets households scale from basic preparedness to whole‑home coverage as needs evolve.
Equally important is sustainability. Choosing battery‑based systems, right‑sizing capacity, integrating solar, and planning for proper recycling all reduce environmental impact while strengthening energy independence. In other words, resilience and sustainability are no longer competing goals—they reinforce each other.

Summary & Call to Action
- Trend: The UK is moving decisively from noisy, fossil‑fuel standby generators to clean, portable power stations. Growth is strong, and adoption is broadening from campers and tech enthusiasts to mainstream households.
- Products highlighted: Jackery Solar Generator 500 (essentials), 1000 Pro (balanced family use), 2000 Plus (scalable resilience). Each serves a distinct profile, and together they cover most UK household scenarios.
- What to do next: Map your outage risks, list priority loads, and choose a capacity tier that matches reality with a 20–50% buffer. Prefer LiFePO₄‑based systems with UKCA certification and app monitoring; add solar where feasible. Test your setup quarterly.
- Why it matters: A well‑chosen home generator safeguards health, productivity, and comfort during grid disruptions—while advancing a greener, quieter, and more self‑reliant way of living.
Preparedness is not pessimism; it’s smart planning. By investing in the right home generator—ideally paired with solar—you equip your household to weather storms, manage uncertainty, and contribute to the UK’s transition toward a low‑carbon future.