A simple cut can reveal a lot about the tool behind it. Clean lines, smooth edges, or rough breaks all depend on choosing the right equipment.
Saw types play a quiet but important role in shaping how materials respond during cutting.
Each design serves a specific purpose, influenced by blade structure, movement, and control.
Some focus on careful precision, others favor speed or strength.
Knowing how saw types differ helps reduce effort, improve accuracy, and support safer handling.
The sections ahead gradually unfold how these tools vary and why each has a place in different cutting tasks.
What Are Saw Types?
Saw types refer to the different kinds of saws designed for specific cutting tasks.
Each type is shaped and built to cut certain materials, such as wood, metal, plastic, or stone.
Some saws are moved by hand, while others use electricity or batteries to power the blade.
Saw types are often grouped based on how the blade moves, the teeth pattern, and the kind of cut produced.
For example, some saws are made for straight cuts, while others handle curves or angled cuts.
Choosing the correct saw type helps achieve cleaner results, improves safety, and reduces material waste during cutting work.
Different Saw Types
This section outlines the main saw types, highlighting how each tool differs in design, cutting method, and purpose, making it easier to compare options and match them to specific cutting needs:
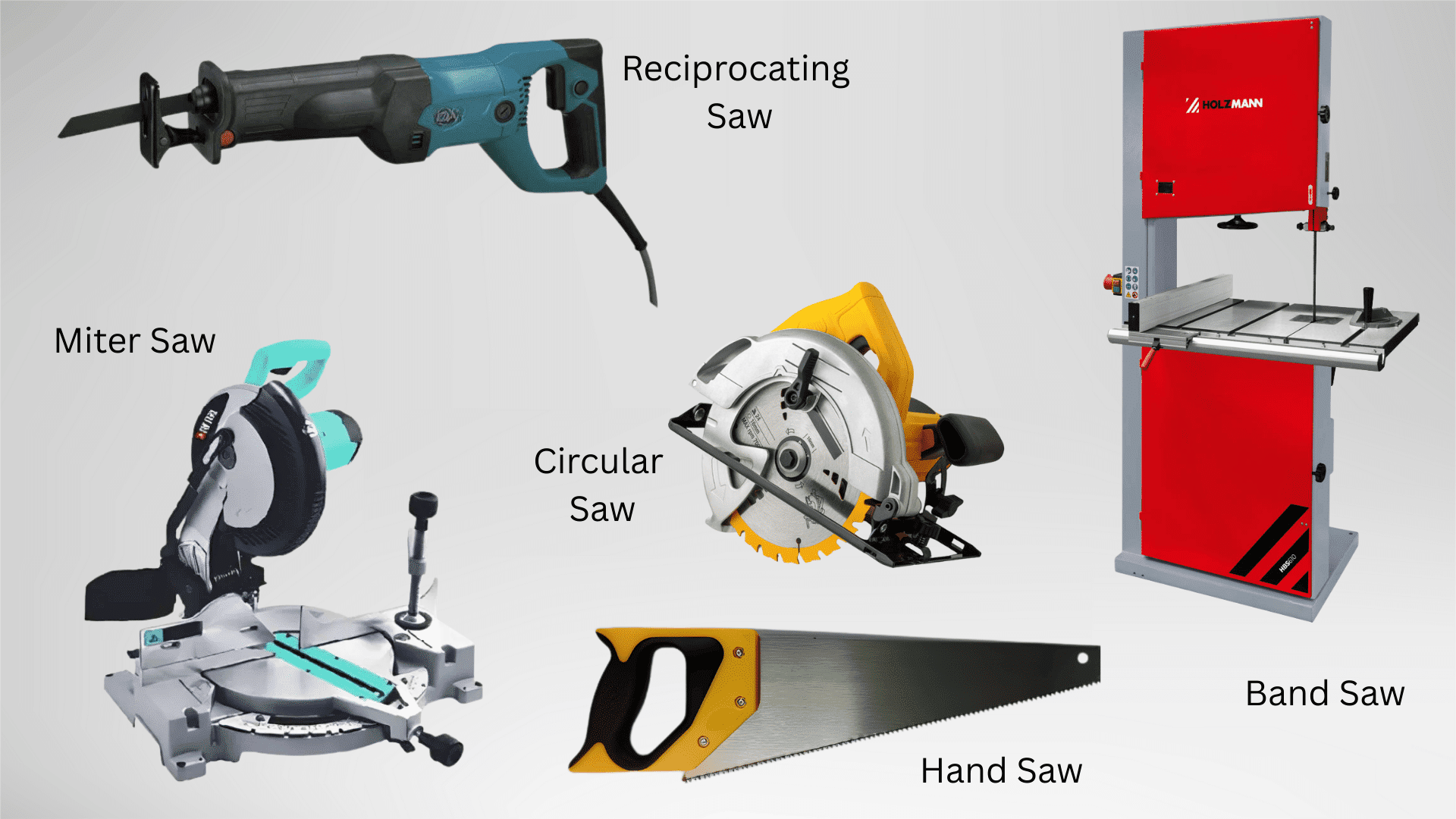
1. Hand Saw
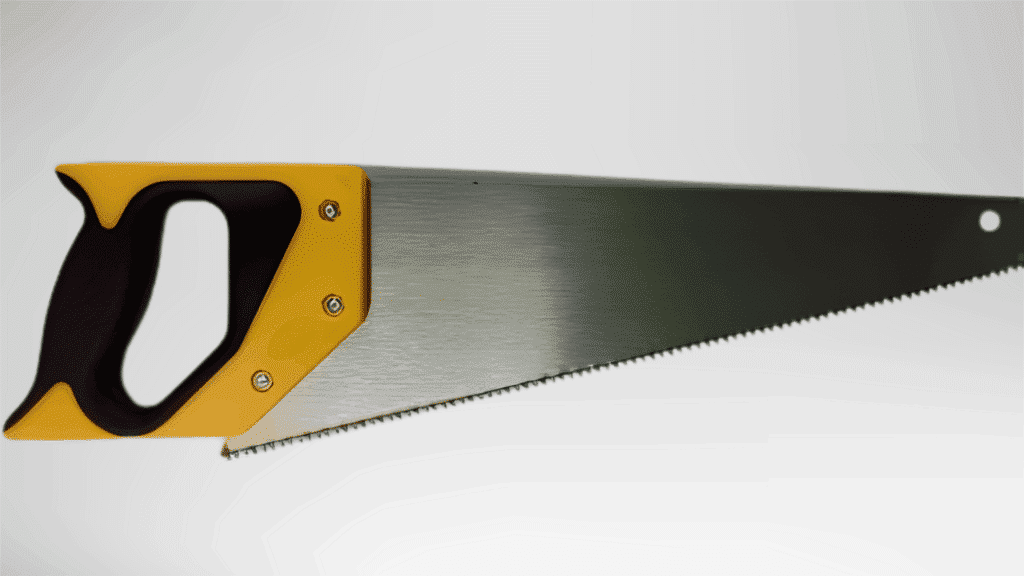

A hand saw is a manual cutting tool used for controlled cutting without power support.
It features a straight blade and a firm handle that allows steady movement during use.
This saw suits tasks where accuracy matters more than speed. It is easy to carry, simple to maintain, and works well for basic cutting needs.
The tool remains useful in small projects and situations where power tools are not practical or available.
Best For:
- Manual cutting tasks
- Small woodworking jobs
- Basic home repairs
Common Applications:
- Cutting wooden boards
- Trimming planks
- Furniture adjustments
2. Crosscut Saw
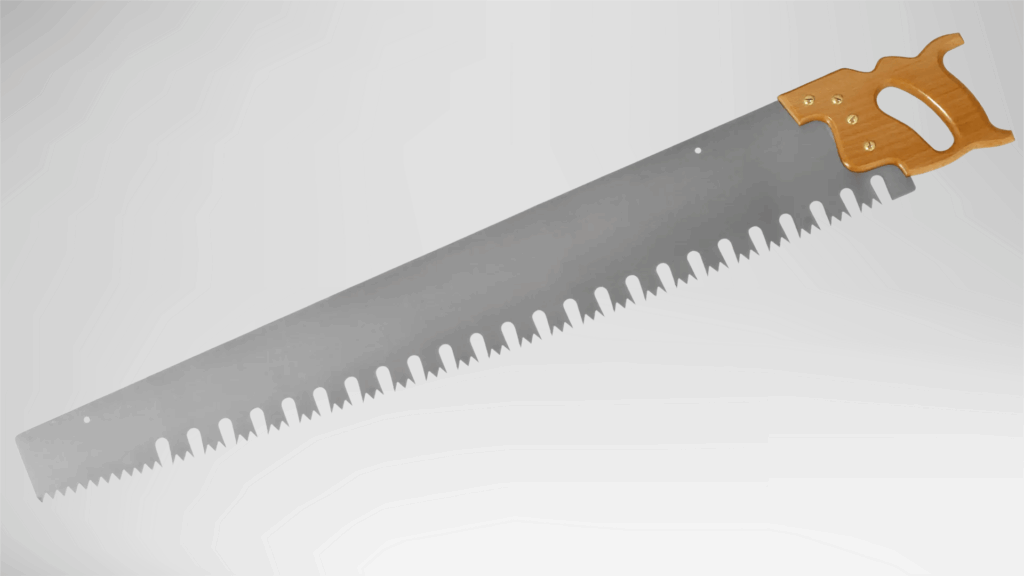

A crosscut saw is designed to cut wood across the grain using angled teeth that slice through fibers cleanly.
This structure helps reduce rough edges and improve surface quality. It works well for preparing wood pieces to length and handling thicker materials.
The saw is commonly used in both indoor and outdoor settings where clean cuts are required.
Its design supports steady cutting with consistent results.
Best For:
- Cutting across the wood grain
- Producing smooth edges
- Traditional carpentry tasks
Common Applications:
- Cutting logs
- Sizing lumber
- Wood framing work
3. Rip Saw
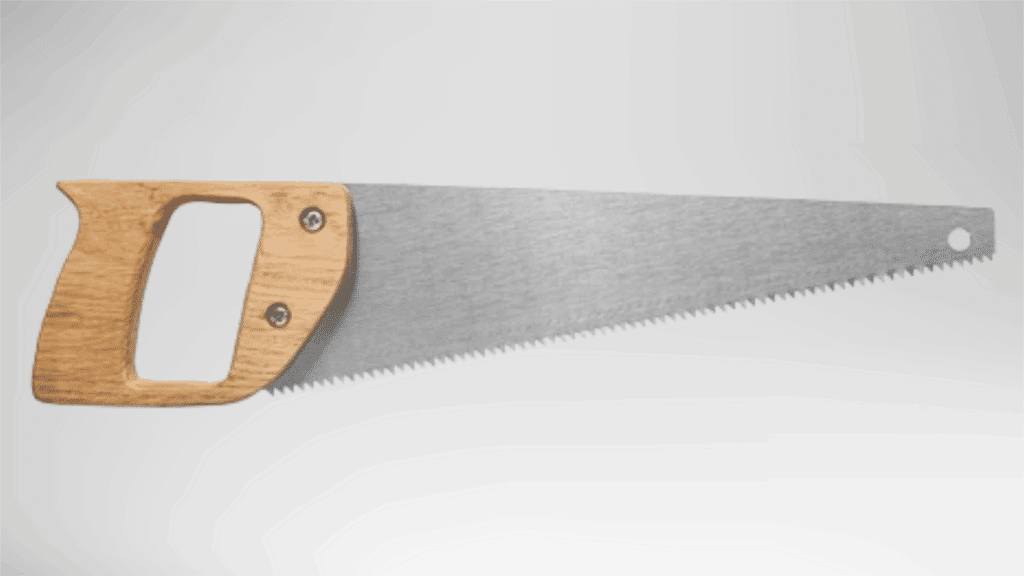

A rip saw is built for cutting wood along the grain using large, chisel-shaped teeth.
This design allows faster material removal compared to other hand saws. It focuses on efficiency rather than surface finish.
The saw performs well when breaking down wide boards into narrower sections.
It is commonly used in workshops where wood needs to be resized before shaping or joining.
Best For:
- Lengthwise wood cutting
- Fast material separation
- Straight wood cuts
Common Applications:
- Splitting wooden boards
- Preparing lumber
- Workshop sizing tasks
4. Hacksaw
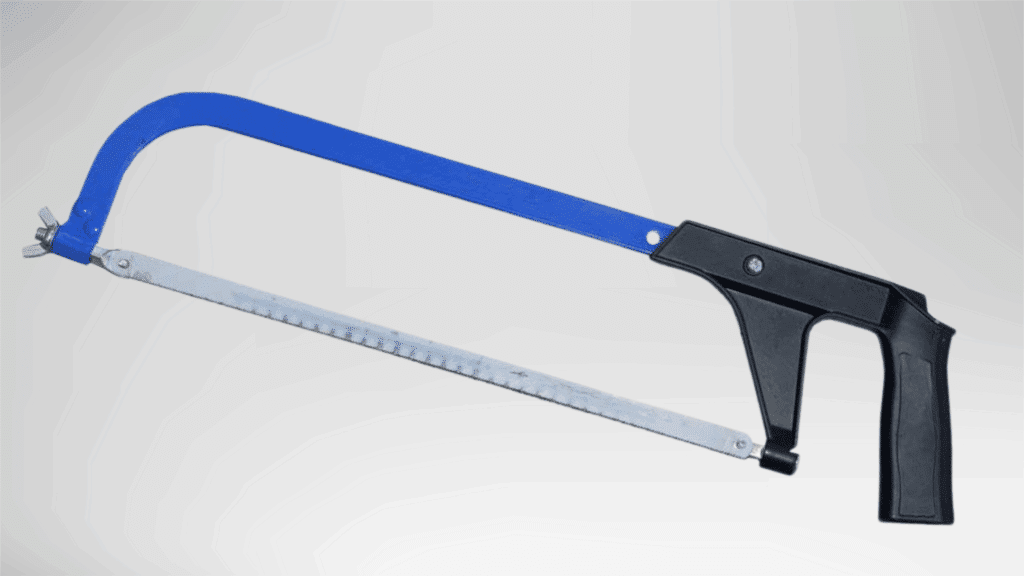

A hacksaw is a fine-toothed saw mounted in a metal frame, made for cutting hard materials.
The thin blade allows controlled movement and access to tight spaces. It provides accuracy when working with metal or plastic parts.
The tool is widely used in repair and maintenance tasks where precision matters.
Blade tension can be adjusted to improve cutting performance and stability.
Best For:
- Cutting hard materials
- Precise manual cuts
- Narrow working areas
Common Applications:
- Cutting metal pipes
- Trimming bolts
- Plastic component work
5. Coping Saw
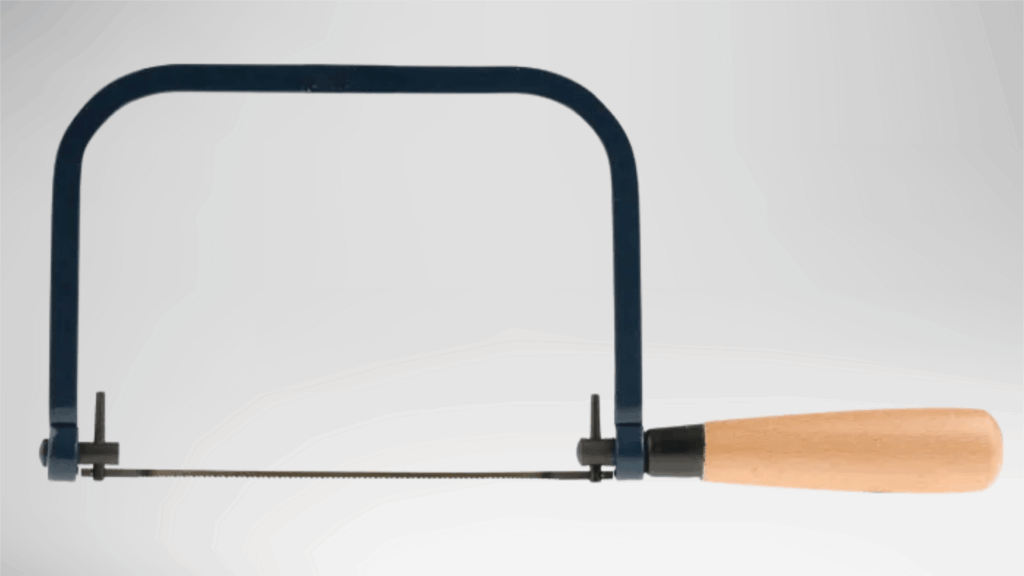

A coping saw is a lightweight hand saw designed for detailed and curved cutting work.
It has a thin blade held under tension within a U-shaped frame, allowing sharp direction changes during cutting.
This saw works well for tasks that require precision rather than speed.
The narrow blade helps handle tight corners and intricate shapes. It is commonly used in fine woodworking where controlled movement and accuracy are important.
Best For:
- Curved cutting work
- Detailed wood shaping
- Precision-focused tasks
Common Applications:
- Cutting decorative patterns
- Trimming moldings
- Craft and hobby projects
6. Bow Saw
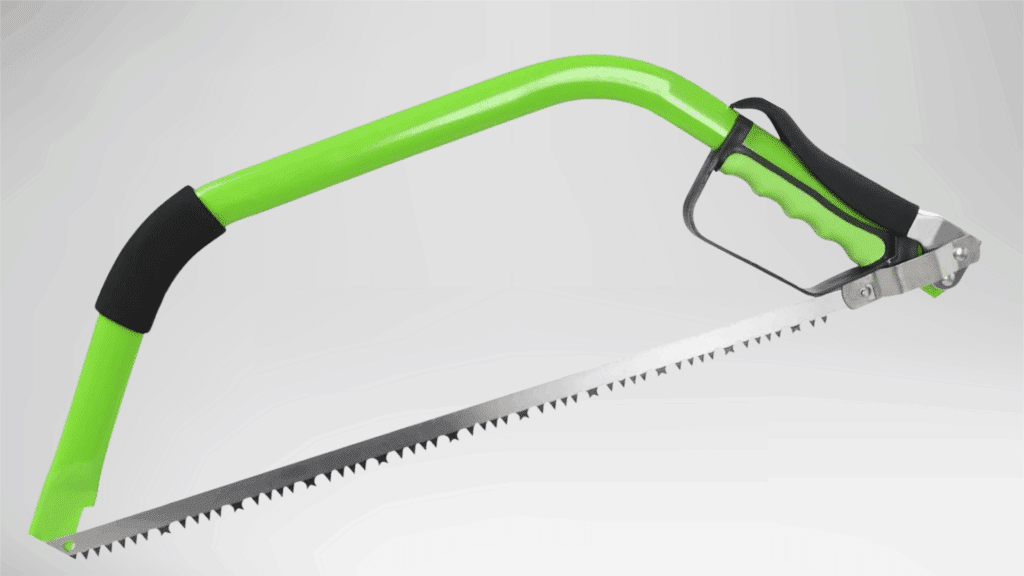

A bow saw is a sturdy hand saw with a long blade supported by a metal frame. It is built for cutting thicker materials with steady force.
The blade design allows efficient cutting through rough wood.
This saw is often used outdoors and handles heavy cutting tasks better than smaller hand saws.
Its structure supports durability and control during extended use.
Best For:
- Cutting thick wood
- Outdoor woodwork
- Rough cutting tasks
Common Applications:
- Cutting branches
- Processing firewood
- Garden maintenance
7. Japanese Saw
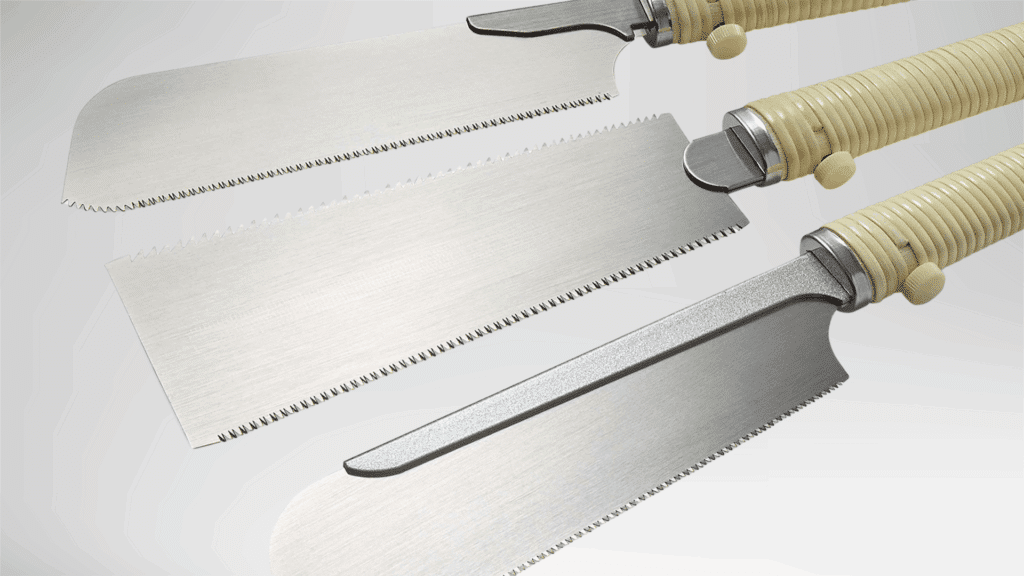

A Japanese saw is a precision hand saw that cuts on the pull stroke rather than the push stroke.
This cutting style improves control and reduces effort.
The thin blade produces clean and narrow cuts. It is valued for accuracy and smooth results.
The saw suits tasks where fine detail and clean finishes are required, especially in woodworking environments.
Best For:
- High-accuracy cutting
- Fine woodworking
- Clean-edge results
Common Applications:
- Joinery work
- Furniture making
- Detail wood cutting
8. Keyhole Saw
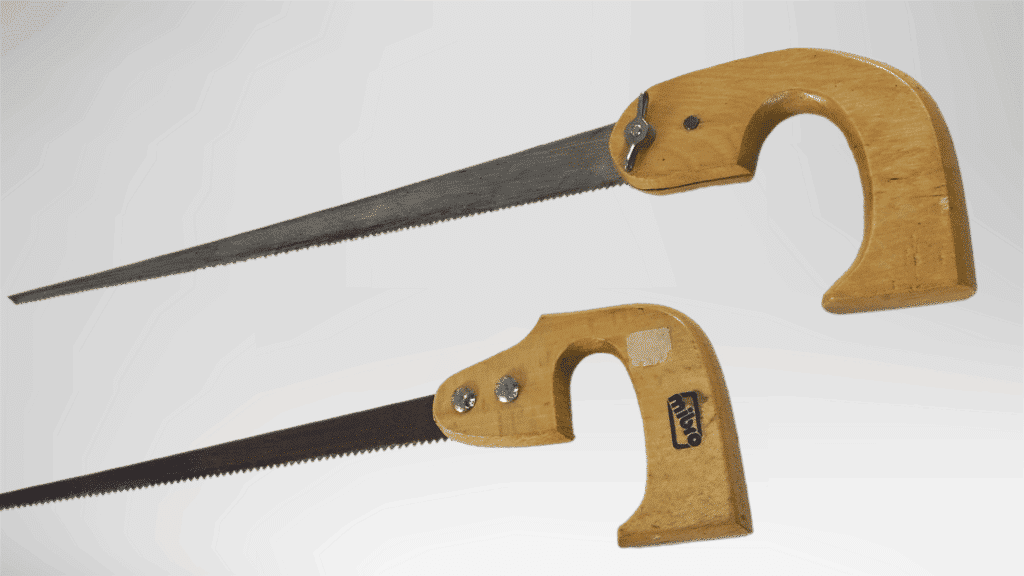

A keyhole saw is a narrow hand saw designed for cutting small openings in flat surfaces.
Its pointed blade allows easy starting without drilling large entry holes.
The saw works well for controlled interior cuts where space is limited. It provides flexibility when working on surfaces that cannot be removed.
This tool is commonly used in finishing and installation tasks that require accuracy in confined areas.
Best For:
- Cutting small openings
- Interior surface work
- Tight cutting spaces
Common Applications:
- Drywall openings
- Vent cutouts
- Electrical box fitting
9. Back Saw
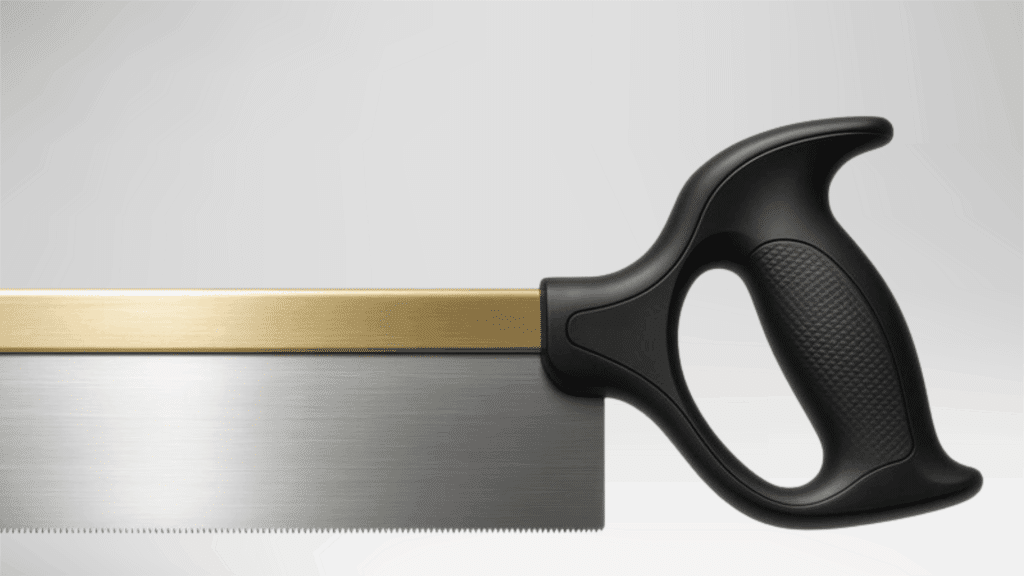

A back saw is a hand saw with a reinforced spine along the top of the blade.
This added support improves stability and straightness during cutting.
The saw produces clean, accurate cuts and suits tasks that require precision.
It is commonly used in controlled woodworking environments. The design helps maintain alignment while cutting thinner wood pieces.
Best For:
- Straight precision cuts
- Controlled woodworking
- Fine joinery tasks
Common Applications:
- Cutting joints
- Trimming wood edges
- Furniture assembly
10. Pruning Saw
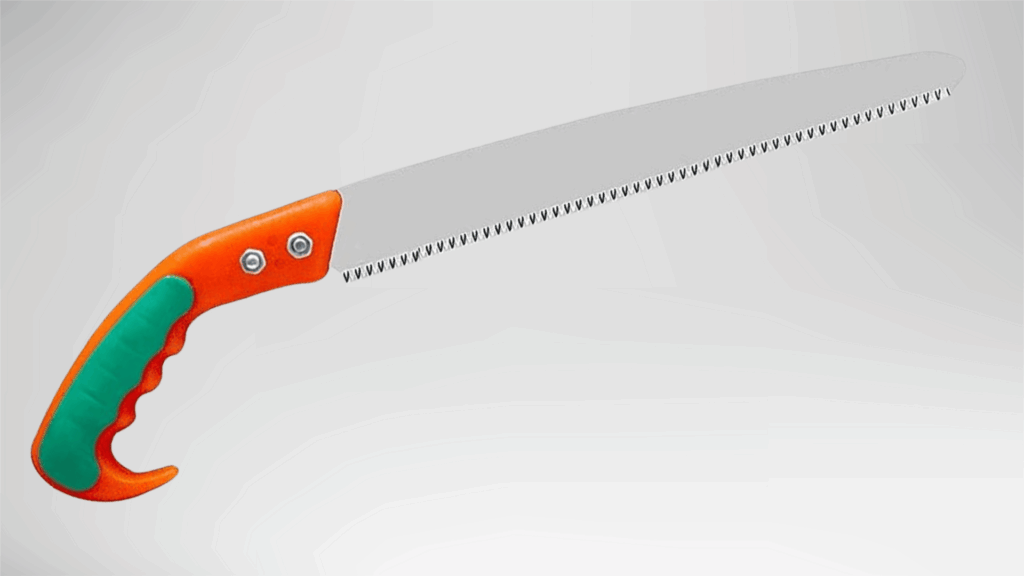
A pruning saw is designed for cutting living wood efficiently.
It features sharp teeth that cut on the pull or push stroke, depending on design. The blade shape allows smooth cutting through branches.
This saw is lightweight and easy to handle outdoors. It works well for garden care where clean cuts help support plant health.
Best For:
- Cutting live branches
- Outdoor trimming tasks
- Garden maintenance
Common Applications:
- Tree pruning
- Shrub shaping
- Branch removal
11. Circular Saw
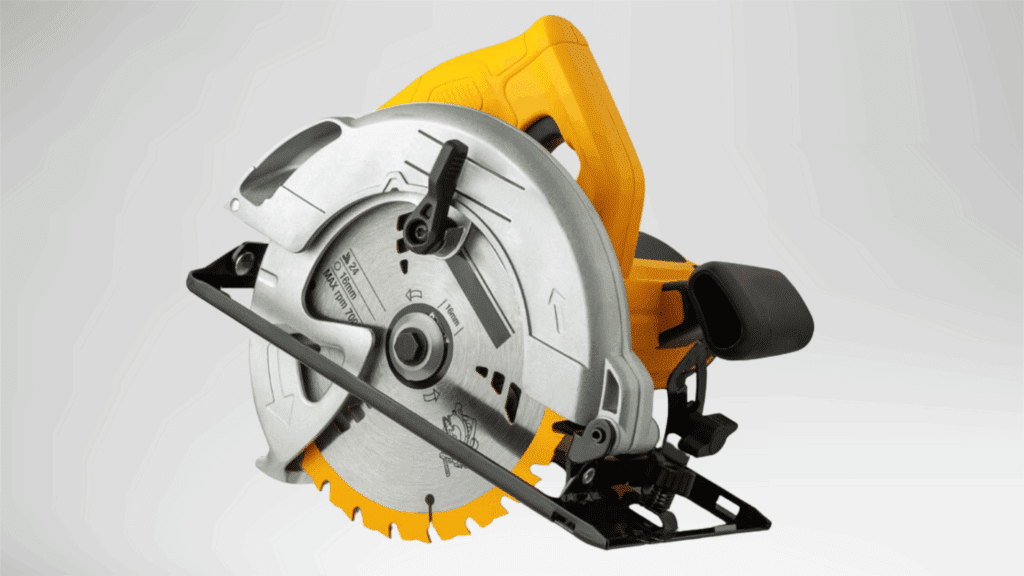

A circular saw is a powered cutting tool that uses a rotating round blade. It is designed for fast, straight cuts through various materials.
The saw offers strong cutting performance while remaining portable.
It is commonly used on job sites and in workshops where speed and accuracy are required.
Blade depth and angle adjustments allow flexibility for different cutting needs.
Best For:
- Fast straight cuts
- Portable power cutting
- General construction tasks
Common Applications:
- Cutting plywood
- Sizing lumber
- Sheet material work
12. Jigsaw
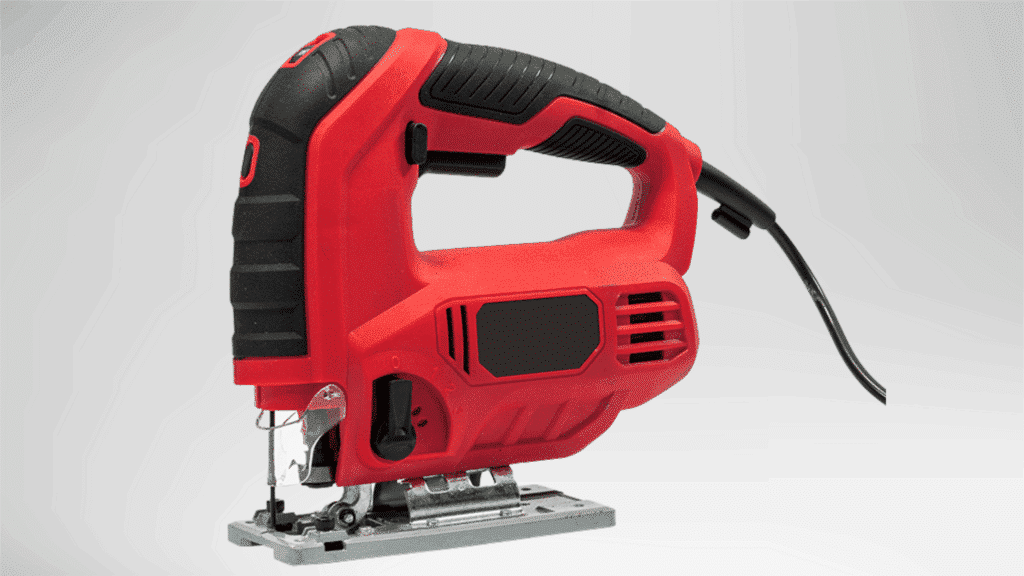

A jigsaw is a powered saw that moves its blade up and down to create curved or irregular cuts.
The narrow blade allows detailed shaping and internal cutouts.
It works well on thinner materials and supports controlled movement.
The saw is easy to handle and suits projects that need flexibility rather than straight-line cutting.
Best For:
- Curved cutting work
- Detailed shaping
- Internal cutouts
Common Applications:
- Cutting patterns
- Shaping panels
- Decorative projects
13. Miter Saw
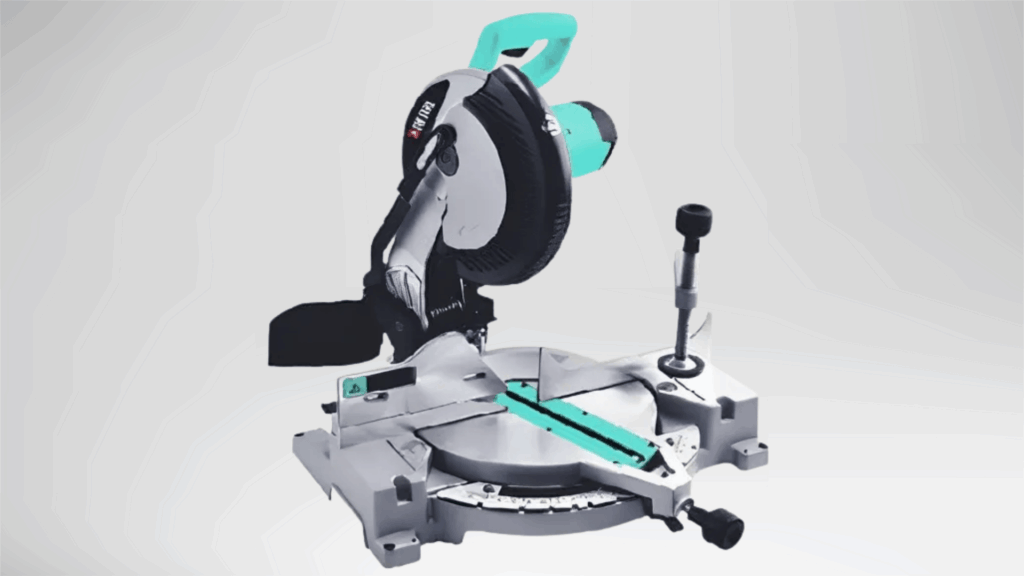
A miter saw is a stationary power tool designed for accurate angle and cross cuts. It uses a circular blade mounted on a pivoting arm.
The saw delivers consistent results and is widely used for precision cutting.
Angle settings allow repeatable cuts with minimal effort. It is commonly used where accuracy is essential.
Best For:
- Angle cutting tasks
- Repeatable cuts
- Precision trimming
Common Applications:
- Cutting trim
- Framing pieces
- Molding work
14. Table Saw
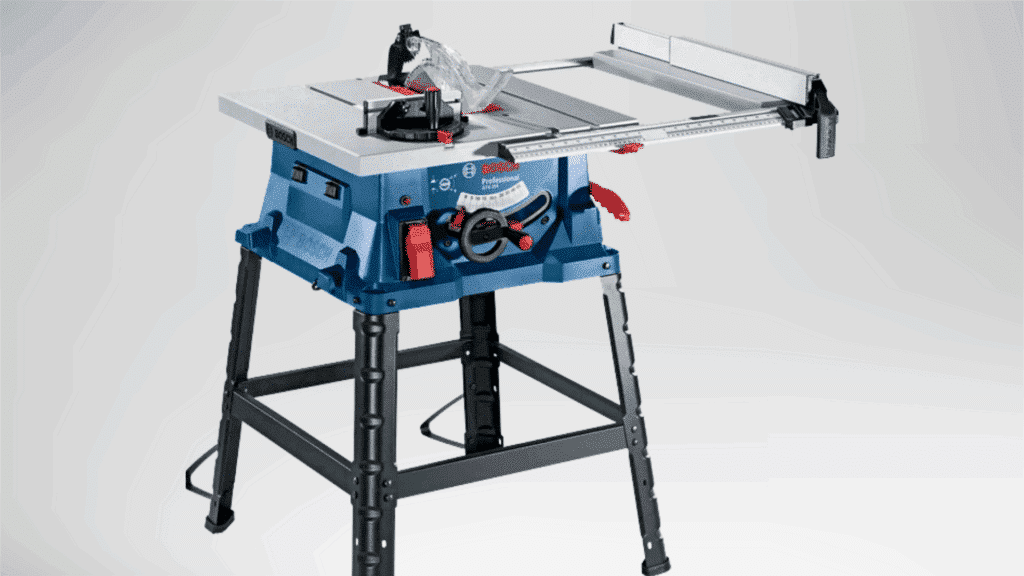

A table saw is a stationary power tool with a circular blade mounted through a flat surface.
It allows material to be guided steadily through the blade for accurate cuts.
This saw is known for precision and consistency. Fence and blade height adjustments support controlled cutting.
It is commonly used in workshops that require repeated straight cuts with uniform results.
Best For:
- Accurate straight cuts
- Repeated cutting tasks
- Workshop-based work
Common Applications:
- Ripping boards
- Sizing panels
- Wood processing
15. Reciprocating Saw
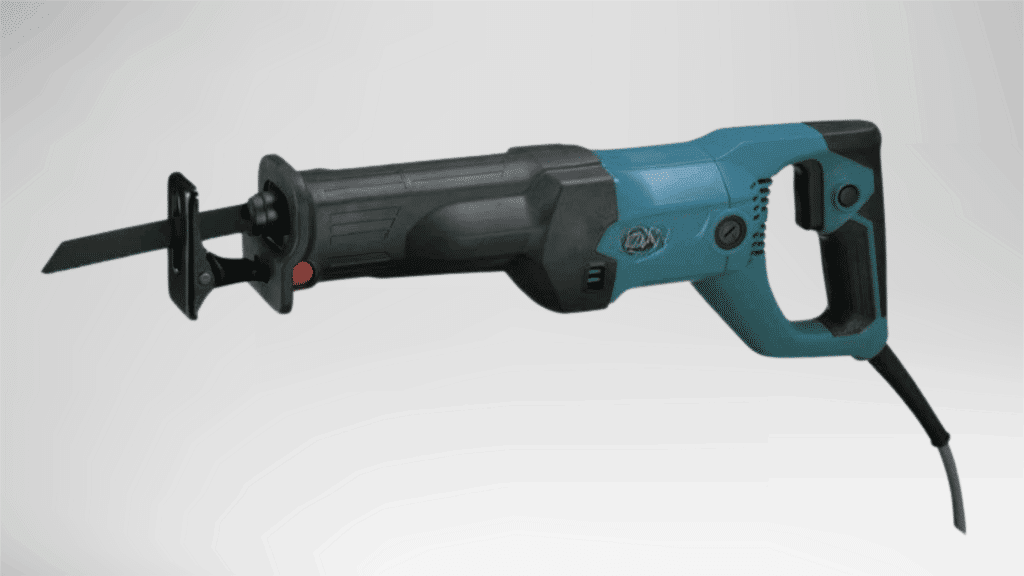

A reciprocating saw uses a push-and-pull blade motion to cut through materials quickly. It is designed for rough cutting where speed matters more than finish quality.
The saw is easy to maneuver and works well in tight or awkward positions.
It is often used for tasks that involve dismantling or cutting through mixed materials.
Best For:
- Rough cutting tasks
- Quick material removal
- Confined work areas
Common Applications:
- Demolition work
- Pipe cutting
- Material removal
16. Band Saw
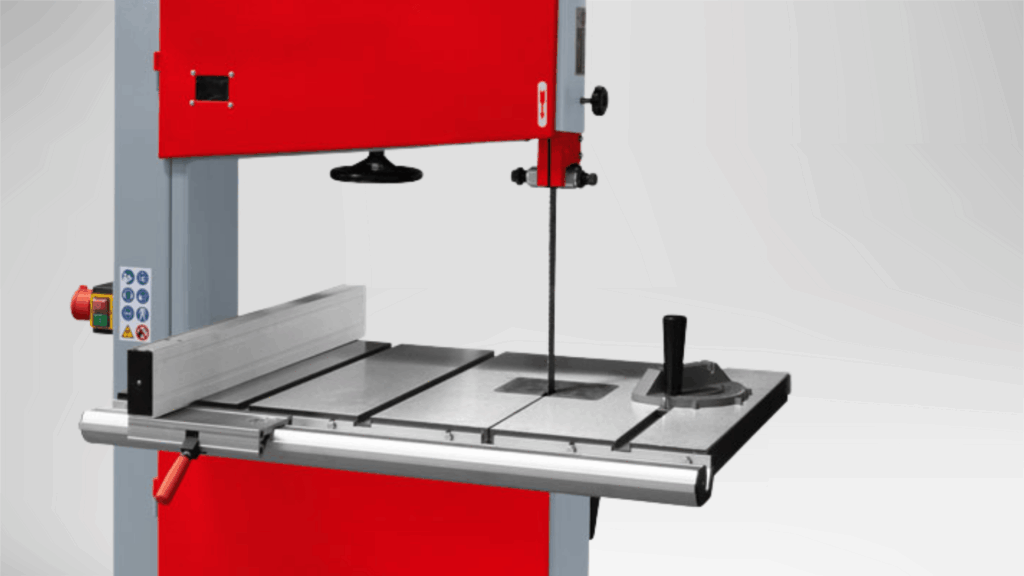
A band saw uses a continuous loop blade stretched over two wheels. It allows both straight and curved cuts with smooth control.
The saw supports cutting thicker materials and maintains accuracy over long cuts.
It is commonly found in workshops that handle detailed shaping and consistent cutting tasks.
Best For:
- Smooth curved cuts
- Thick material cutting
- Controlled shaping
Common Applications:
- Resawing wood
- Shaping components
- Workshop cutting
How to Choose the Right Saw Type?
Choosing the right saw type depends on the kind of work being done and the material involved.
Some saws are made for straight cuts, while others handle curves or rough cutting.
The working space, skill level, and need for speed or accuracy also play a role.
Using the correct saw helps improve results, reduces effort, and supports safer cutting.
Understanding basic differences makes selection easier and more practical for everyday tasks.
Key points to consider:
- Material being cut
- Type of cut required
- Manual or powered option
- Workspace size
- Comfort and control
Choosing a suitable saw ensures smoother work, better control, and dependable results while supporting safer handling and efficient completion of cutting tasks.
Conclusion
Every cutting task carries its own demands, and the right tool often makes the difference between smooth progress and unnecessary effort.
Throughout this blog, saw types were outlined based on design, cutting motion, and practical use.
From hand-operated options suited for controlled work to power-driven saws built for speed and consistency, each type serves a clear role.
Matching the saw to the material, cut style, and working environment helps improve results while supporting safer handling.
Instead of relying on guesswork, selecting from the many saw types becomes easier with clear comparisons and real use cases. Each tool earns its place through function, not complexity.
Share your experience or favorite saw type in the comments below.