In the era of Industry 4.0, automation systems have become the backbone of modern manufacturing, smart factories, and industrial operations. Among the critical components that power these systems, induction motors hold a significant place. Their robustness, reliability, and cost-effectiveness make them indispensable in a wide range of automation applications. This article explores the role of induction motors in modern automation systems, highlighting their working principles, advantages, applications, and future trends.
Understanding Induction Motors
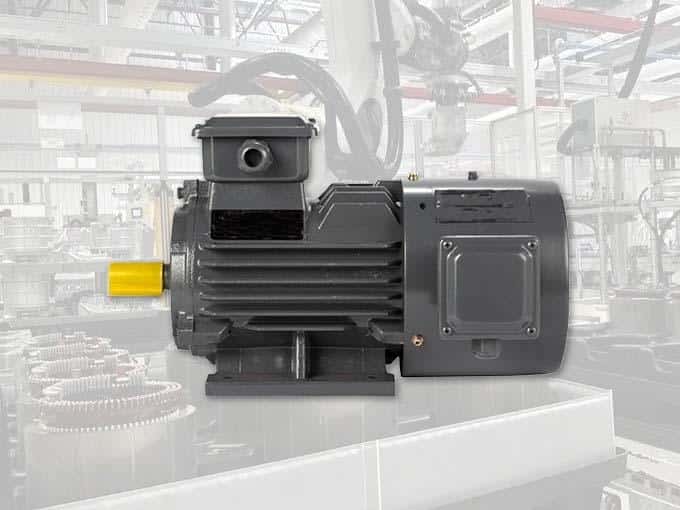
An induction motor, also known as an asynchronous motor, is an electric motor in which the electric current required to produce torque is induced by electromagnetic induction rather than supplied directly to the rotor. Induction motors are classified primarily into two types:
- Squirrel Cage Induction Motors: The rotor resembles a cage, typically made of laminated iron and conducting bars. It is widely used in industrial applications due to its simple design and low maintenance requirements.
- Wound Rotor Induction Motors: The rotor has windings connected through slip rings, allowing for variable speed control and higher starting torque. These variable speed motors are used in applications requiring precise speed regulation.
The working principle of induction motors is based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the stator winding, it generates a rotating magnetic field. This field induces a current in the rotor, creating torque that drives the mechanical load.
Why Induction Motors Are Essential in Automation
Modern automation systems demand precise, reliable, and efficient motion control. Induction motors meet these requirements for several reasons:
1. Reliability and Durability
Induction motors are known for their robustness and long operational life. Unlike other motor types, they have no brushes, which reduces wear and tear, maintenance costs, and operational interruptions. This reliability is crucial in automated manufacturing processes where downtime can lead to significant productivity losses.
2. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a top priority in modern industrial operations. Induction motors are highly efficient, especially when used with variable frequency drives (VFDs) to match motor speed with the required load. This capability not only reduces electricity consumption but also minimizes operational costs.
3. Low Maintenance
Automation systems thrive on consistent performance with minimal human intervention. Induction motors require less maintenance compared to DC motors or servo motors, making them ideal for automated systems running continuously in factories or industrial plants.
4. Wide Range of Applications
From conveyor belts and pumps to robotic arms and HVAC systems, induction motors can drive various automation equipment. Their versatility allows them to adapt to multiple industrial sectors, including manufacturing, packaging, material handling, and chemical processing.
5. Compatibility with Advanced Control Systems
Integration with advanced control systems, such as PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition), is seamless with induction motors. These motors can be controlled accurately using VFDs, providing precise speed regulation and torque control, essential for automated processes that require high accuracy and synchronization.
Applications of Induction Motors in Automation
Induction motors are integral to numerous automated operations. Here are some key applications:
1. Manufacturing and Assembly Lines
Automated manufacturing relies heavily on induction motors to drive conveyor belts, robotic arms, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). The consistent speed, torque, and durability of these motors ensure smooth production flow and minimal downtime.
2. Material Handling Systems
In warehouses and distribution centers, induction motors power conveyor systems, hoists, and cranes. Their ability to handle varying loads efficiently and reliably makes them ideal for transporting heavy materials in automated environments.
3. Pumps and HVAC Systems
Automation extends to utilities as well. Induction motors drive pumps for fluid transfer and HVAC systems for climate control in industrial facilities. VFD-controlled induction motors ensure optimal energy usage, contributing to sustainable and cost-effective operations.
4. Robotics and Machine Tools
While servo motors dominate high-precision robotics, induction motors are still widely used in automated machine tools where robust and reliable motion is required. For example, lathes, milling machines, and automated cutters often utilize induction motors for their dependable performance under continuous operation.
5. Packaging and Processing Lines
Food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries rely on automated packaging and processing lines. Induction motors drive filling machines, labeling systems, and packaging conveyors, ensuring speed, accuracy, and repeatability in operations.
Advantages of Using Induction Motors in Automation Systems
The widespread adoption of induction motors in automation is driven by several advantages:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Induction motors are generally less expensive than DC or servo motors, providing an economical solution for industrial automation.
- High Starting Torque: Especially in wound rotor types, induction motors can handle heavy startup loads, critical in applications like conveyors and crushers.
- Robust Design: Induction motors withstand harsh industrial environments, including dust, heat, and vibration.
- Scalability: Available in a wide range of power ratings, from fractional horsepower for small devices to thousands of kilowatts for heavy industrial machinery.
- Integration with VFDs: When paired with variable frequency drives, induction motors achieve precise speed and torque control, enhancing automation flexibility.
Future Trends
The role of induction motors in automation continues to evolve with advancements in technology:
- Smart Motors: Integration with IoT devices allows real-time monitoring of motor performance, predictive maintenance, and energy optimization.
- Energy-Efficient Designs: New materials and design innovations are improving efficiency, reducing energy losses, and supporting sustainable industrial practices.
- AI-Driven Automation: Artificial intelligence is being used to optimize motor operation in complex automation systems, further increasing productivity and reducing operational costs.
- Hybrid Systems: Induction motors are increasingly combined with other motor types or regenerative braking systems to enhance performance in specialized applications.

Conclusion
In modern automation systems, induction motors remain a cornerstone technology. Their reliability, energy efficiency, low maintenance requirements, and adaptability make them ideal for driving industrial operations across various sectors. From manufacturing lines and material handling systems to HVAC and robotic applications, induction motors ensure smooth, efficient, and cost-effective automation.
As industries continue to embrace digitalization and smart manufacturing, the role of induction motors is only set to grow. With advancements in VFD technology, IoT integration, and AI-driven control, these motors will remain a critical component in shaping the future of industrial automation.
Investing in high-quality induction motors and understanding their capabilities is crucial for any business looking to optimize automation, reduce downtime, and achieve operational excellence.